40 maps that explain the Middle East
At its height, the Islamic State - also known as ISIS, ISIL, or Daesh - held about a third of Syria and 40 percent of Iraq. By December 2017 it had lost 95 percent of its territory, including its two biggest properties, Mosul, Iraq's second largest city, and the northern Syrian city of Raqqa, its nominal capital. The following is a timeline of the rise, spread and and fall of the Islamic State.

Mohammed, Arab Conquests, Islamic Conquests, and Civil War in the Early Middle Ages
World history Course: World history > Unit 3 Lesson 4: Spread of Islam The spread of Islam The rise of Islamic empires and states Spread of Islamic Culture The development and spread of Islamic cultures Key concepts: the spread of Islam Focus on continuity and change: the spread of Islam Arts and humanities > World history >

MapSpread of Islam Diagram Quizlet
In 1154, Arab Muslim geographer al-Idrisi, working at the behest of King Roger of Sicily, created a huge map of the known world. The map was more than 9 feet long and composed of 70 separate section maps. The Library preserves a 1928 recreation of this map.
15 European Countries With Most Muslims WorldAtlas
Compare Pricing, Inventory and Datasheets for Millions of In-Stock Parts. Octopart Is The Preferred Search Engine for Electronic Parts.
9 questions about the ISIS Caliphate you were too embarrassed to ask Vox
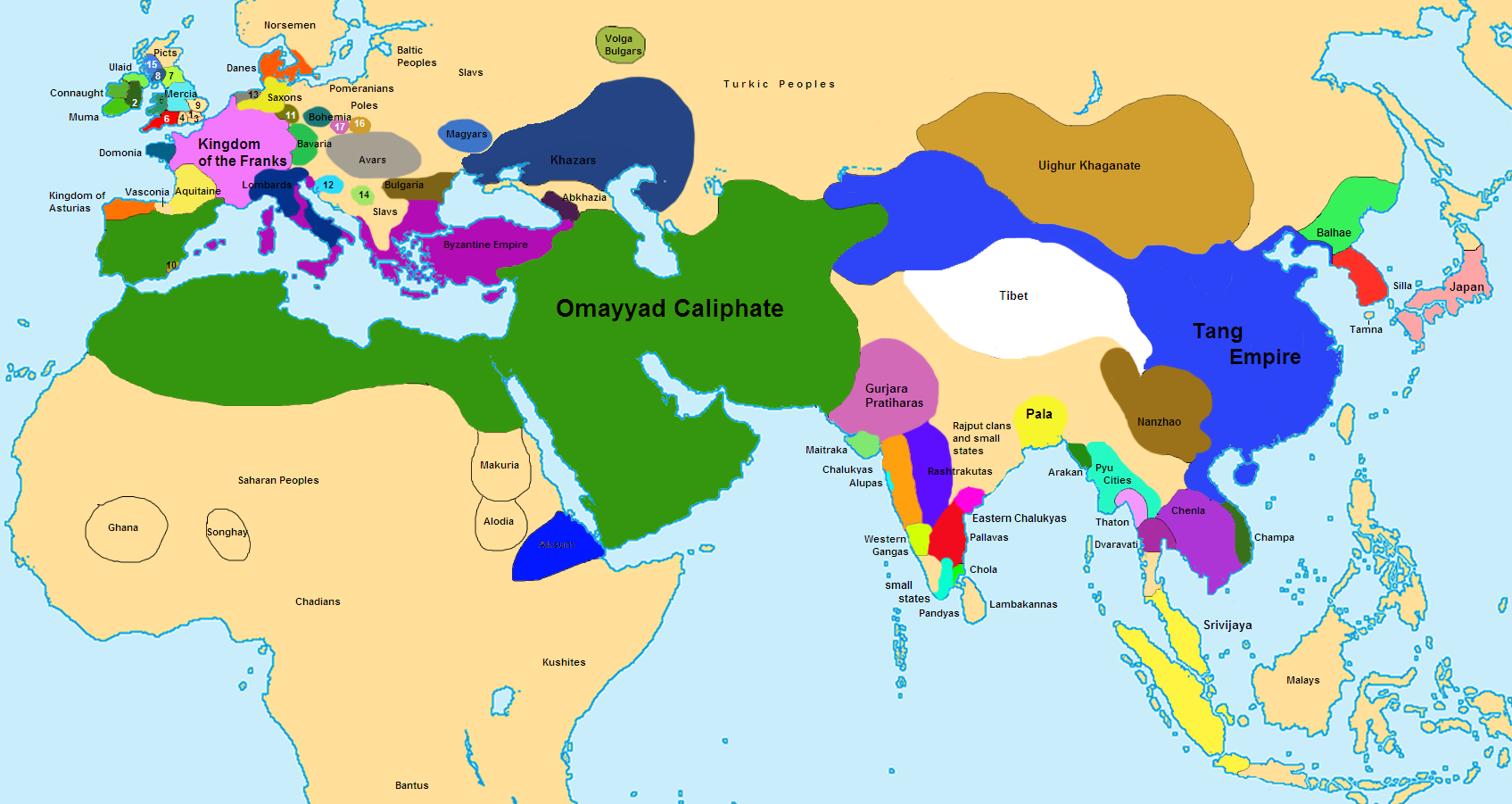
This article includes a list of successive Islamic states and Muslim dynasties beginning with the time of the Islamic prophet Muhammad (570-632 CE) and the early Muslim conquests that spread Islam outside of the Arabian Peninsula, and continuing through to the present day. [citation needed]

Islamic world History, Population, & Map Britannica
Adherence to Islam is a global phenomenon: Muslims predominate in some 30 to 40 countries, from the Atlantic eastward to the Pacific and along a belt that stretches across northern Africa into Central Asia and south to the northern regions of the Indian subcontinent.
Mohammed, Arab Conquests, Islamic Conquests, and Civil War in the Early Middle Ages
"The Silk Roads" Map Description: Land routes (indicated by red lines) and water routes (indicated by blue lines) retrace the "extensive interconnected network of trade routes . . . connecting East, South, and Western Asia with the Mediterranean world, as well as North and Northeast Africa and Europe" ("Silk Road").
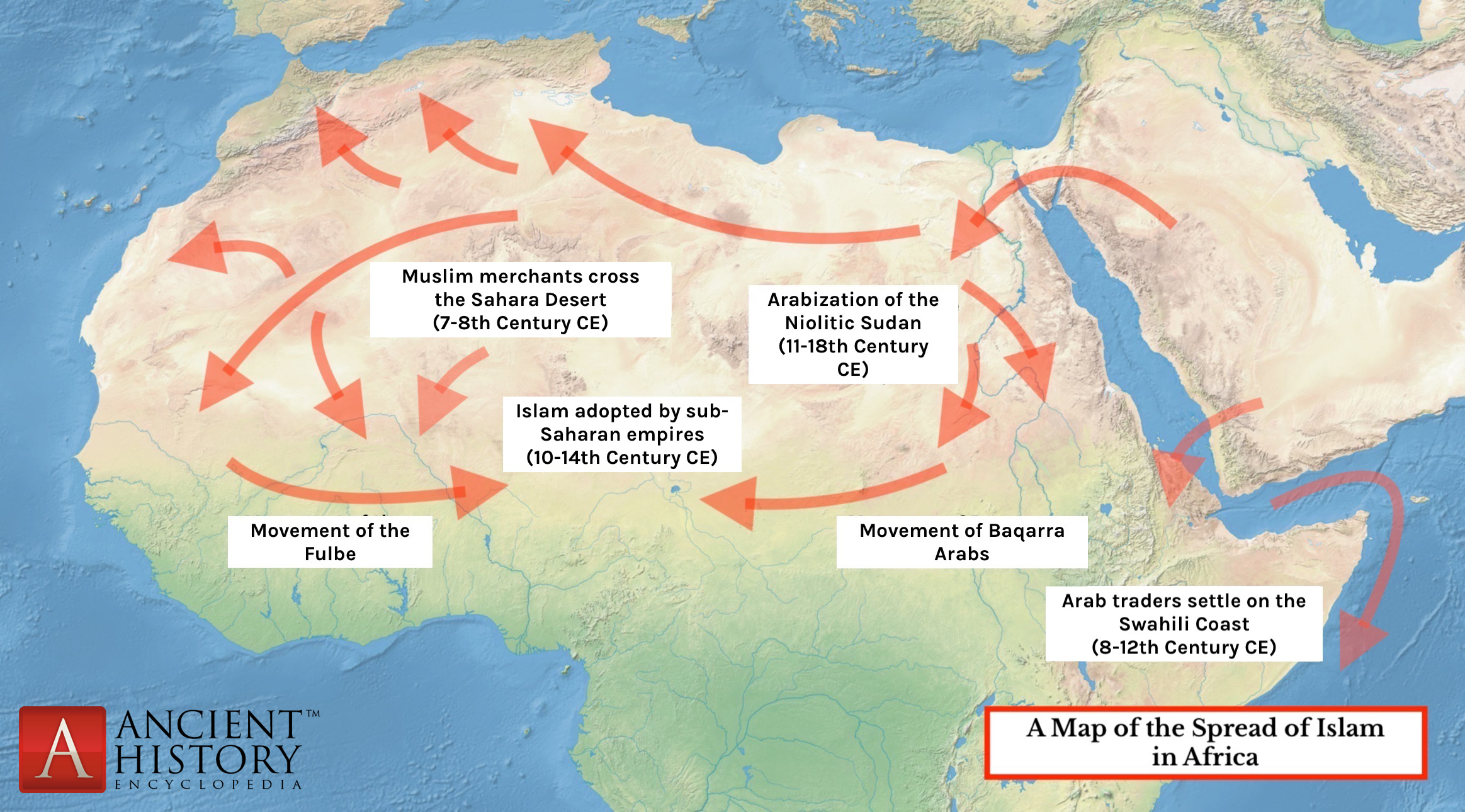
The Spread of Islam in Africa (Illustration) World History Encyclopedia
¡Precios increíbles y alta calidad aquí en Temu. Envío gratuito en todos los pedidos. No deslizar. Enormes descuentos en nuestros productos aquí - ¡hasta un 90% de descuento!
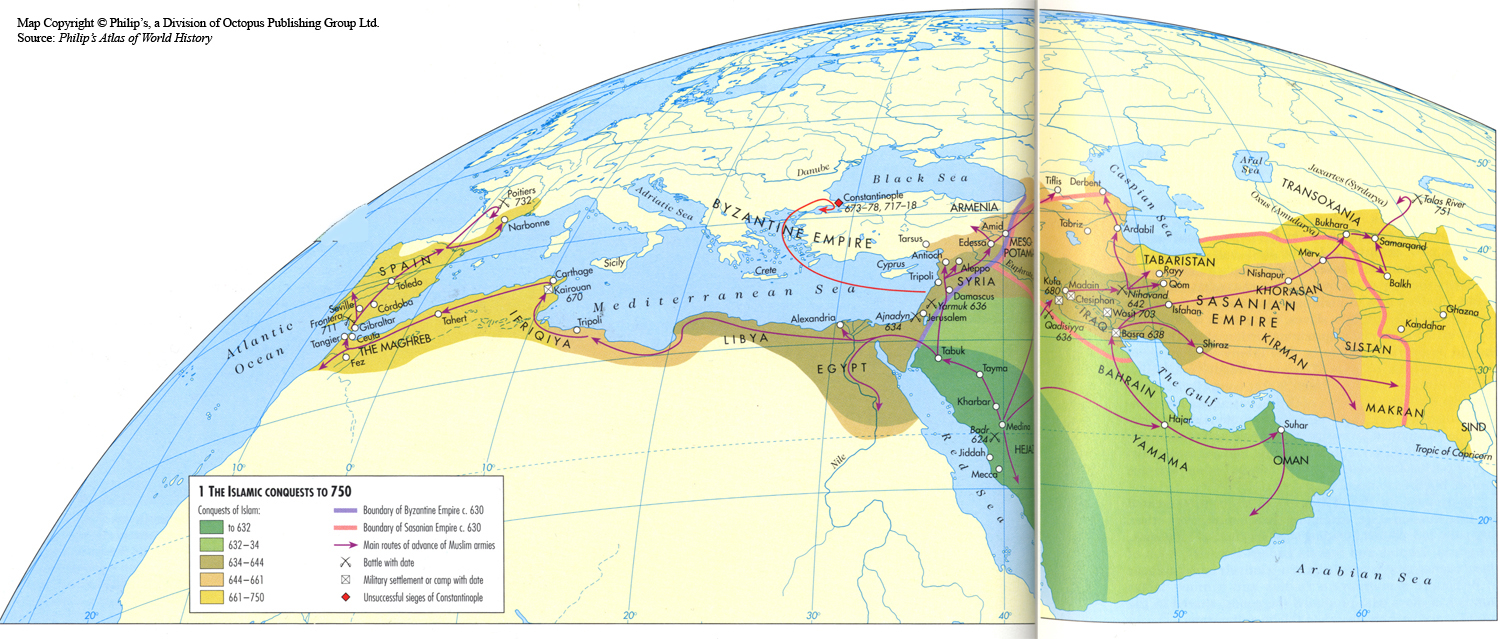
EUH 4310 Weekly Topics Florin Curta
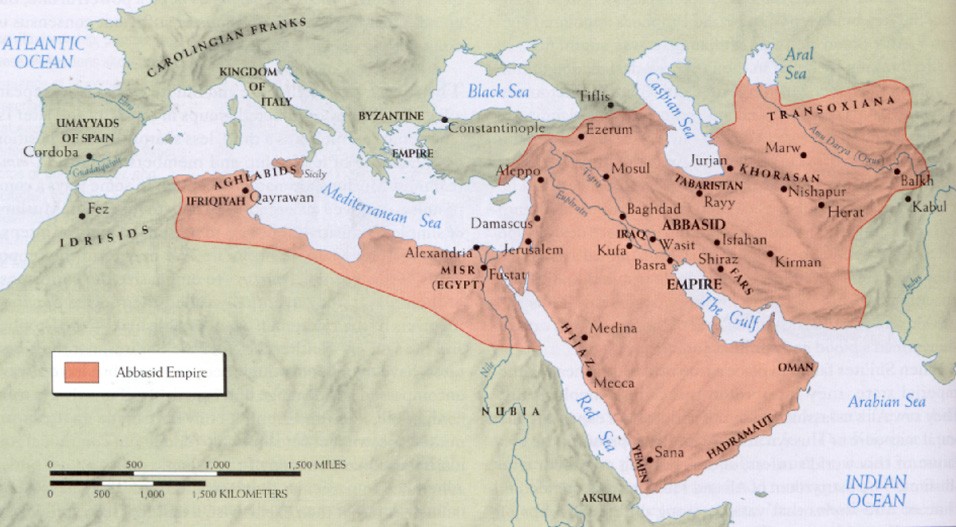
Abbasid Caliphate The Abbasid Caliphate ( / əˈbæsɪd / or / ˈæbəsɪd /; Arabic: الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, romanized : al-Khilāfah al-ʿAbbāsiyyah) or Abbasid Empire was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad.

Islamic Empires Test Diagram Quizlet
Netchev, Simeon. " Islamic Conquests in the 7th-9th Centuries ." World History Encyclopedia. World History Encyclopedia, 08 Jun 2021. Web. 06 Jan 2024. A map illustrating the rise and expansion of early Islamic caliphates from the Prophet Muhammad until the 9th century.
Daniel's Four Kingdoms
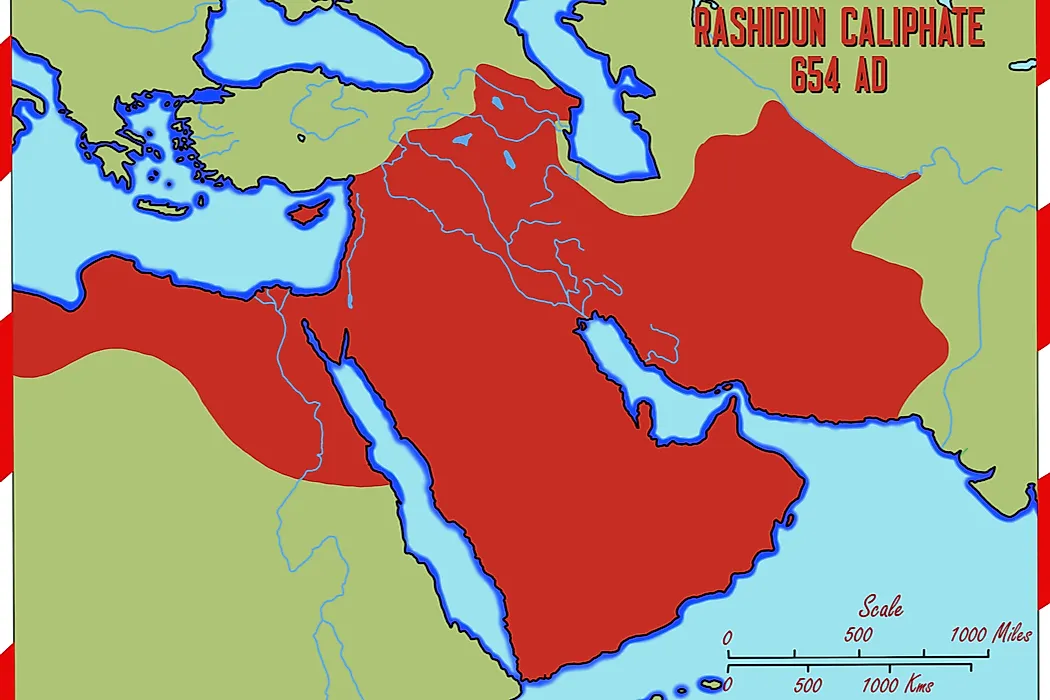
The crucial early years of Islamic expansion were overseen by the first four caliphs, a group of rulers who came to be called the "rightly guided" or Rashidun.These four figures— Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and the originally overlooked son-in-law of Muhammad, Ali —ruled between 632 and 661, a period when much Byzantine and Persian territory was conquered, and the message of Islam spread.
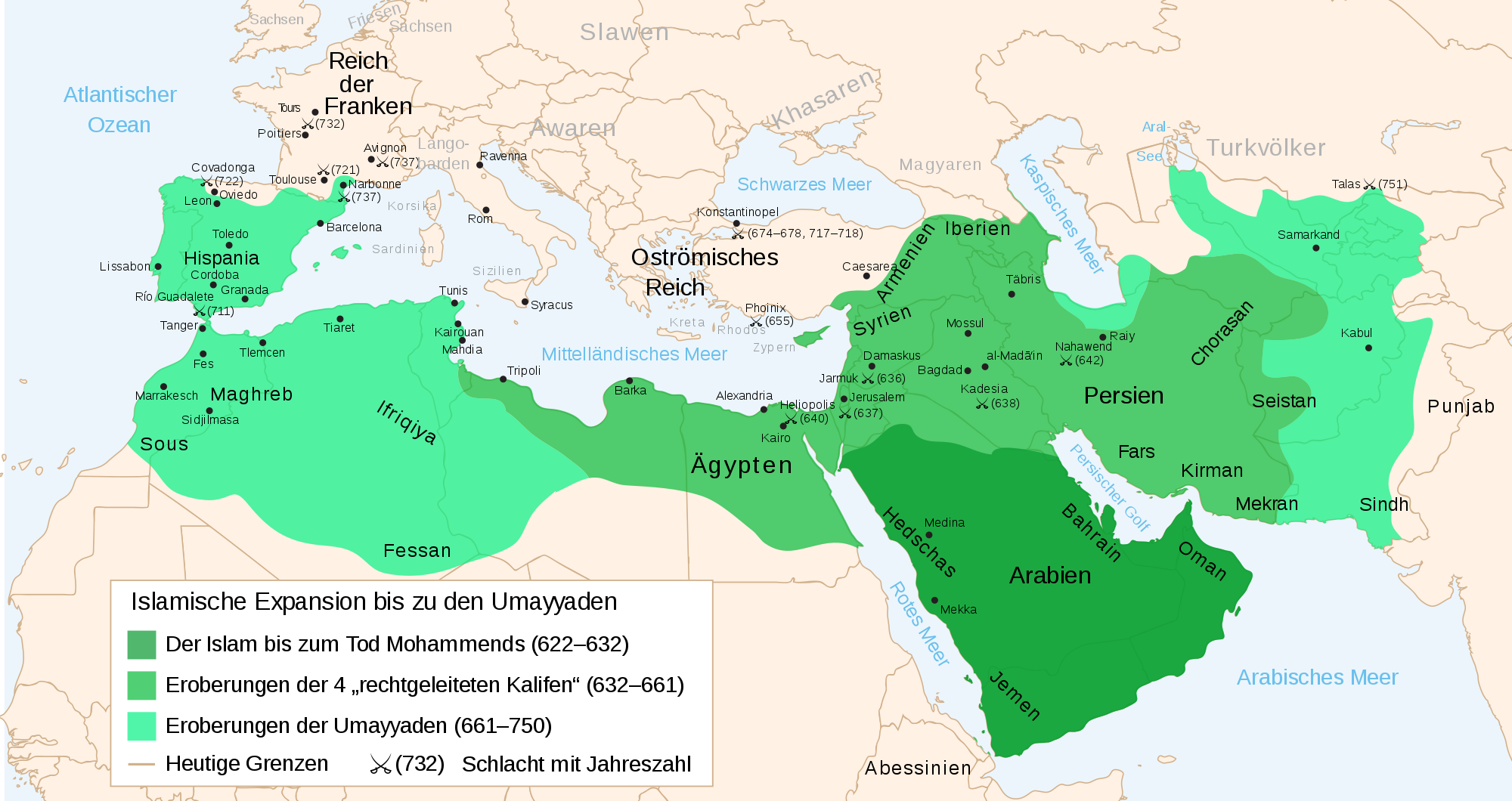
Umayyad Conquest, 7th & 8th Centuries CE (Illustration) World History Encyclopedia
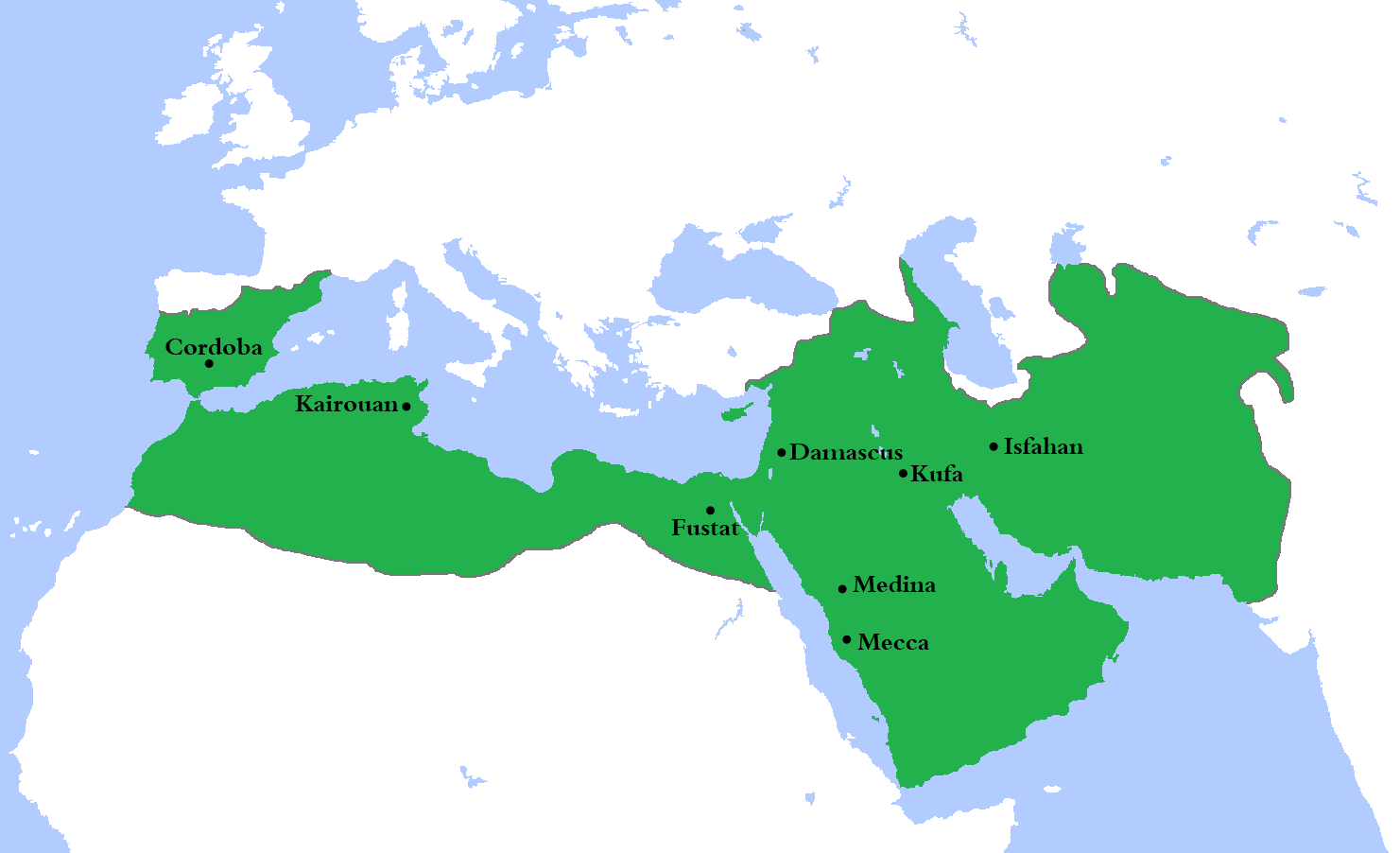
The Caliphate. The Persian empire vanished under the onslaught, and the Byzantine empire lost its most valuable provinces. In their place, the Arabs established a vast empire, called the "Caliphate" ("caliph" means "successor", in this case to the Prophet Muhammed). Up until now the Caliphate has been ruled from Damascus, in Syria.

301 Moved Permanently
The Tabula Rogeriana, by Al-Idrisi in 1154, is one of the most detailed maps of the ancient world. This map has been rotated to show its similarity with modern maps ( Source) Across the Mediterranean Sea, both Muslims and Christians were making portolan charts, navigational maps with no agenda other than ensuring a safe voyage.

How the battle against the Islamic State is redrawing the map of the Middle East The
Early on in Islamic history, under the Rashidun caliphate —the reign of the first four caliphs, or successors, from 632 to 661 CE—and the Umayyad caliphate, Arab Muslim forces expanded quickly. With the Abbasids, more non-Arabs and non-Muslims were involved in the government administration.
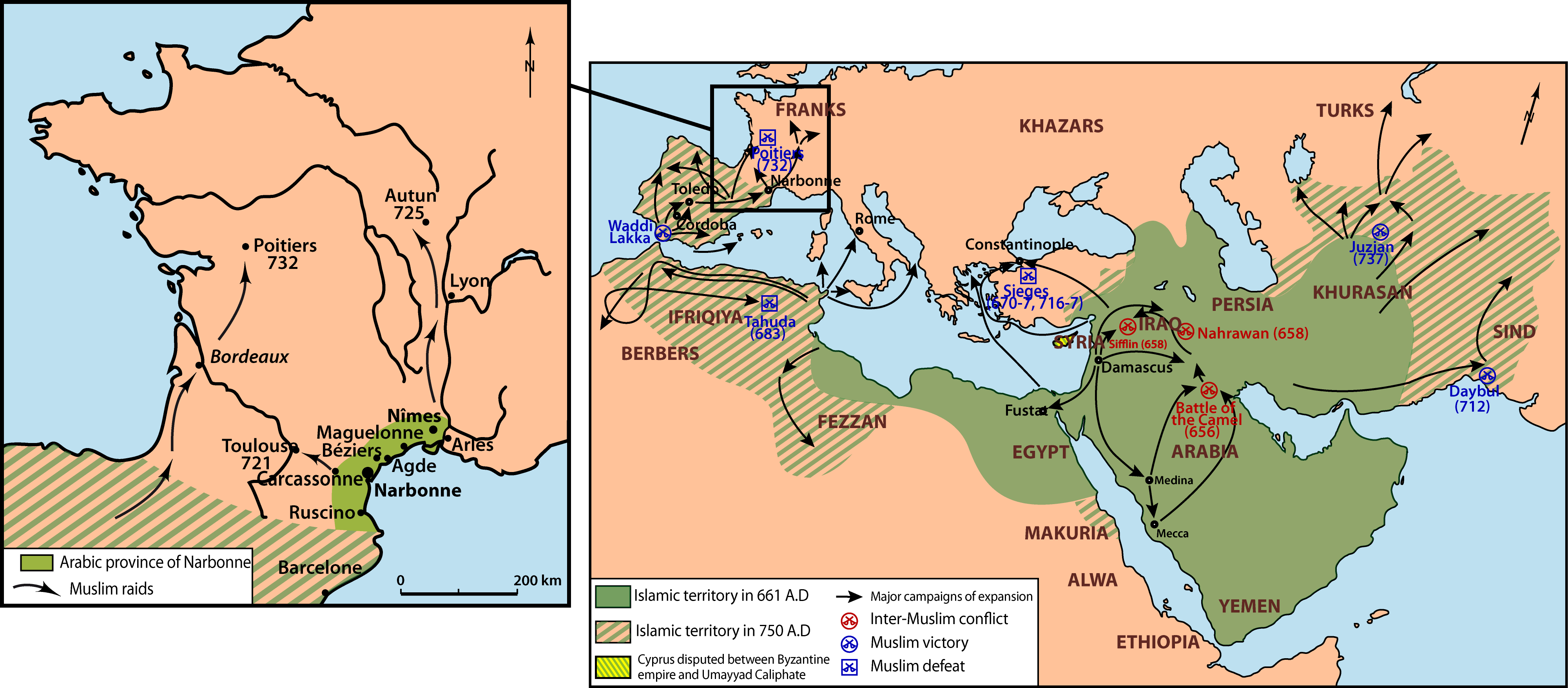
Medieval Muslim graves in France reveal a previously unseen history Ars Technica
The Umayyads continued the Muslim conquests, conquering Ifriqiya, Transoxiana, Sind, the Maghreb and Hispania ( al-Andalus ). At its greatest extent, the Umayyad Caliphate covered 11,100,000 km 2 (4,300,000 sq mi), [1] making it one of the largest empires in history in terms of area. The dynasty was toppled by the Abbasids in 750.
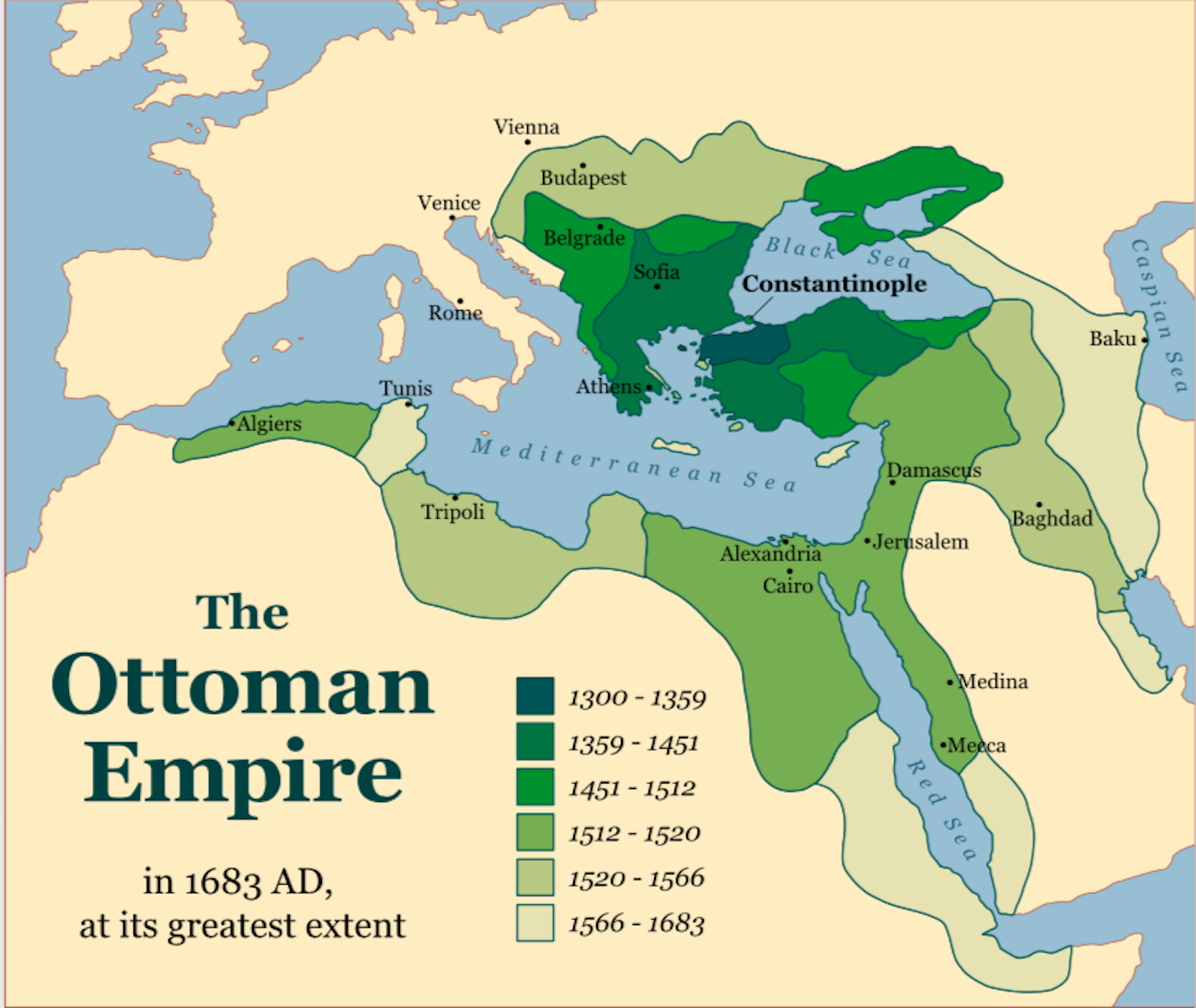
Major Muslim Empires During The Middle Ages WorldAtlas
﮸ This exhibition explores maps of the Islamic World, focusing on the "Gunpowder Empires" of Ottoman Turkey, Safavid Persia, and Mughal India. These empires controlled vast territories during the early modern period (ca. 1500-1800). The Ottoman expanse reigned over Southeastern Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa.